Ductility a Covalent-network Solid a Metallic Solid Both
Which type of solid typically has the lowest melting point of the four types of crystals. Why do solids both brittle and ductile exhibit very high strength under compression as compared to tension.

Plus Two Chemistry Notes Chapter 1 The Solid State A Plus Topper Chemistry Notes Plus Two Chemistry Notes Chemistry
Which of the following properties are typical characteristics of a covalent-network solid a metallic solid or both.

. A ductility b hardness c high melting point. 10th - 11th grade. C-5 pts Sketch a stress-strain curve.
Solid Type of solid Type of particle Bonding between particles Chlorine Cl 2 Molecular Molecule Weak intermolecular forces Silicon dioxide SiO 2 Copper chloride CuCl 2 Potassium K Carbon dioxide CO 2 b Use the information given below to answer the question that follows. 445-453 and 470-75 Zumdahl. Which of the following properties are typical characteristics of a covalent-network solid a metallic solid.
It has a very high melting point of. Covalent solids consist of two- or three-dimensional networks of atoms held together by covalent bonds. Do metals have ductility.
P 426-29440-42 444-47 454 458 see chart. For each of these types of solids indicate the kinds of particles that occupy the lattice points and identify forces among these particles. Covalent network solids are solid compounds containing atoms bonded to each other via covalent chemical bonds.
Hint Ignore the presence of cracks in the solid. Problem 70 Easy Difficulty. I am a great conductor of energy both thermal and electrical.
ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING A. Indicate the type of crystal molecular metallic ionic or covalent-network each of the following would form upon solidification. Practice Distinguishing between Ionic Metallic Covalent Solids with practice problems and explanations.
First week only 499. Which of the following properties are typical characteristics of a. Both covalent-network solids and ionic solids can have melting points well in excess of room temperature and both can be poor conductors of.
Solution for Which of the following properties are typical characteristicsof a covalent-network solid a metallic solid or botha. Both forms are network covalent solids This site shows diagrams of both diamond and graphite structures. You are given a white substance that sublimes at 3000 C.
A ductility b hardness c high melting point. The state of aggregation of solids can be described as belonging to the following four types. Why are Na and K called waxy solids.
BondingInterparticle Forces Review Reference pages. In addition to having high thermal and electrical conductivity and being malleable and ductile they exhibit luster a shiny surface that reflects light. Which of the following properties are typical characteristics of a covalent-network solid a metallic solid or both.
Ductility and malleability Metal crystal structures are flexible layers in the crystal lattice can slide. 4A factor distinguishing a metallic bond from either an ionic or a covalent bond is the mobility of Anonpolar covalent molecules Bionic salts Cpolar covalent molecules Dmetals 5Which is characterized by being insoluble in most solvents and good conductors in the solid state. Diamond is a covalent network solid.
The few exceptions due to it is a liquid metal. Brittleness Metallic compounds are not brittle because the metallic bonds are nondirectional sea of electrons allow the nuclei to move. 92 Network Covalent Ionic and Metallic Solids.
Which type of solid can become an electrical conductor via chemical substitution. They tend to be very hard and have high melting points. Substitutional alloys tend to be more ductile than interstitial alloys.
1264 Which of the following properties are typical characteristics of a covalent-network solid a metallic solid or both. A InAs b MgO c HgS d In e HBr. Both metallic and covalent network solid.
Both Na and K are very soft or ductile. In contrast covalent and ionic bonds which are directional and require specific geometries resulting in fixed three-dimensional lattice structures make many other types of solids brittle so they break under force. 1 ionic 3 covalent network 2 metallic 4 molecular.
The chemical bonding can cause the formation of a network of atoms which leads to the formation of a network solid. Metallic solids have unusual properties. Other examples include silicon quartz and graphite.
These solids have a number of repeating atoms linked to each other via covalent bonds. Most metals that are solids are very ductile. A professional Academic Services Provider.
Ionic solid molecular solid metallic solid O covalent solid Which of the following solids will only conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Which type of solid is more likely to dissolve in water. How could each type of solid be identified in the.
What type of solid did you find. However in other ways their properties are quite different. Up to 256 cash back Get the detailed answer.
The solid is a nonconductor of electricity and is insoluble in water. Both metallic and covalent network solid. Up to 24 cash back 1263 Both covalent-network solids and ionic solids can have melting points well in excess of room.
A ductility b hardness c high melting point. Ametals Bionic salts Cpolar covalent molecules Dnonpolar. A metallic solid or botha ductility b hardness c high melting point.
Network Coordinate Covalent Metallic Bonding. Both covalent-network solids and ionic solids can have melting points well in Both covalent-network solids and ionic solids can have melting points well in excess of room temperature and both can be poor conductors of electricity in their pure form. A ductility b hardness c high melting point.
Question asks Which of the following properties are typical of a Cho Vaillant network solid a metallic solid or both and is docked ill ity which is a metallic solid B is hardness which is both and C is a high melting point which is also both. A network covalent solid consists of atoms held together by a network of covalent bonds pairs of electrons shared between atoms of similar electronegativity and hence can be regarded as a single large moleculeThe classic example is diamond. As you may have guessed metals tend to be both malleable and ductile largely due to the non-directionality of metallic bonds.
Get instant feedback extra help and step-by. Metallic solid molecular solid O ionic solid covalent solid I am very malleable and ductile. A-5 pts Briefly describe compare and contrast ionic covalent and metallic bonding.
Metallic solid or both. High strength with the exception of graphite. Up to 24 cash back Malleability and ductility Metallic compounds are ductile stretchy and malleable bendy because the metallic bonds are nondirectional sea of electrons allow the nuclei to move.
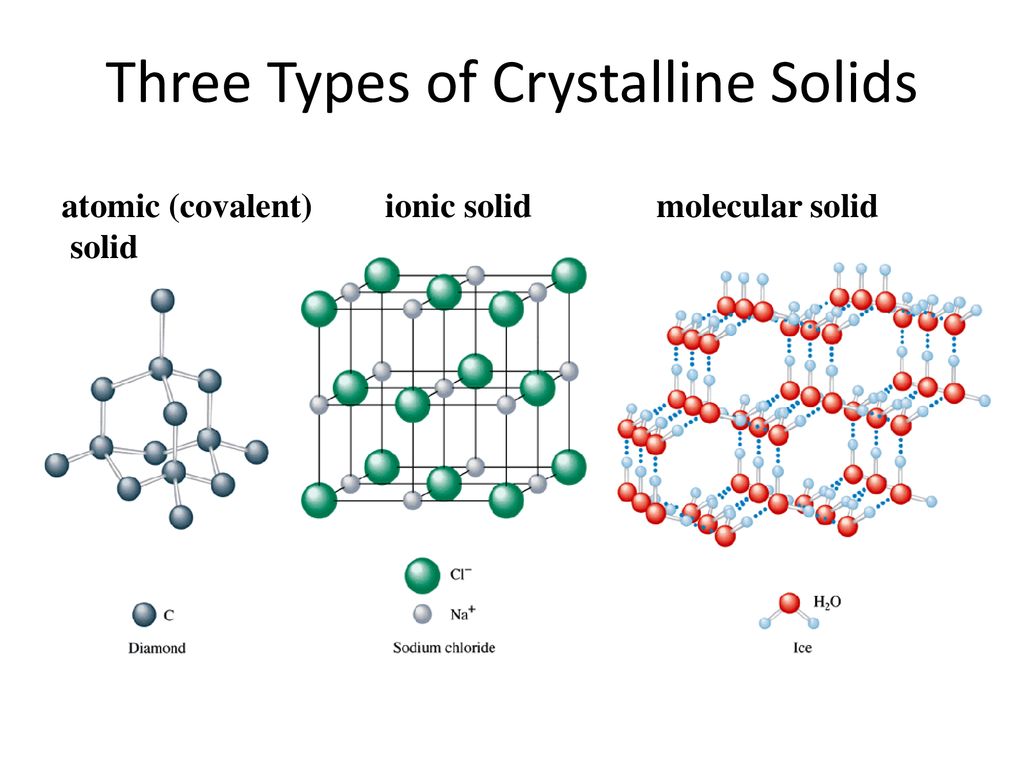
Chapter 3 Solid State Chemistry Week 7 Ppt Download

The Solid State Of Matter Chemistry For Majors Atoms First

Pin By 𝕶𝖔𝖔𝖛𝖎𝖒𝖐 On Black Mamba 美的 Metallic Bonding Black Mamba Positivity
No comments for "Ductility a Covalent-network Solid a Metallic Solid Both"
Post a Comment